Reading-notes
«««< HEAD
text:
Headings :
<h1>This is a Main Heading</h1>
<h2>This is a Level 2 Heading</h2>
<h3>This is a Level 3 Heading</h3>
<h4>This is a Level 4 Heading</h4>
<h5>This is a Level 5 Heading</h5>
<h6>This is a Level 6 Heading</h6>
results is:
This is a Main Heading
This is a Level 2 Heading
This is a Level 3 Heading
This is a Level 4 Heading
This is a Level 5 Heading
This is a Level 6 Heading
** Paragraphs : **
<p>this is a paragraph</p>
result:
this is a paragraph
** Bold & Italic :**
<b> this is bold <b>
<i> this is italic <i>
result:
this is bold
this is italic
Superscript & Subscript :
<sub></sub>
<sup></sup>

When the browser comes across two or more spaces next to each
other, it only displays one space.
Similarly if it comes across a line
break, <br/> it treats that as a single space too. This is known as
white space collapsing.
Quotations :
<blockquote>p>Did you ever stop to think, and forget to start
again? </blockqoute>
result:
p>Did you ever stop to think, and forget to start again?
** Changes to Content :**
<ins> show content that has been inserted into a document
<del>show text that has been deleted from document.
<s> is no longer accurate or relevant (strike through)
introduction to css :
CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
BLOCK & INLINE ELEMENTS :
Block level elements look like they start on a new line.
Examples include the <h1>
Inline elements flow within the text and do not start on a new
line. Examples include <b>
CSS works by associating rules with HTML elements , A CSS rule contains two parts: a selector and a declaration.

using css can be done by 3 ways :
1- Using External CSS <link>
2- Using Internal CSS <style>
3- inline css using style attribute
java script
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one. Each individual instruction or step is known as a statement .
Expressions evaluate into a single value.
JAVASCRIPT IS CASE SENSITIVE
1- COMMENTS:
explain what your code does. They help make your code easier to read and understand.
/* Th i s script displays a greeting to the user based upon the current time.
It is an example from JavaScript & jQuery book */
2- variables:
You can compare variables to short-term memory, because once you leave the page, the browser will forget any information it holds.
syntax

there is many types of varibles :

**3- OPERATORS : **
- ARITHMETIC OPERATORS :
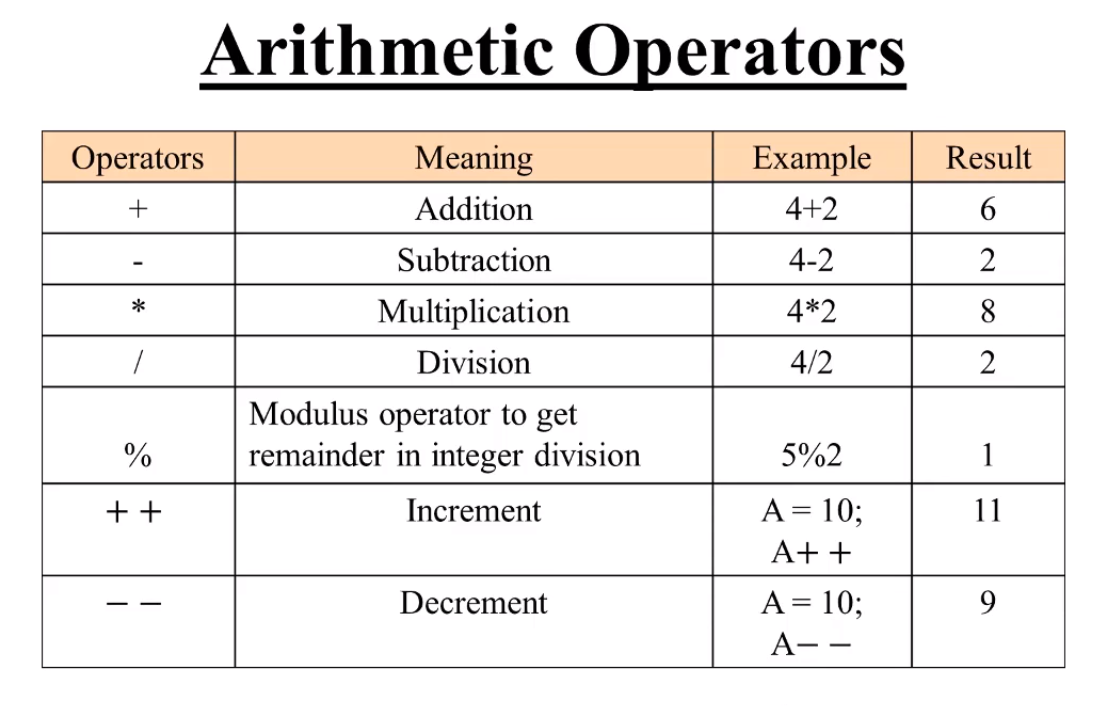
- COMPARISON OPERATORS :

decision-making :
Decision Making statements are** if, else, elseif** and switch these statements are used in making decisions.
there are 2 components to a decision:
1- evaluate of a condition usually done by comparing 2 values using comparison operators.
2- conditional statment if the condtion is met then then the code excute
![decision] (https://i.pinimg.com/originals/d5/da/e2/d5dae2c20b84d9f5b19038de2d38796d.jpg)
var pass = 50; // Pass mark
var score = 90; // Score
// Check if t he user has passed
var hasPas sed = score >= pass ;
// Wr ite the message i nto the page
var el = document .getElementByld(' answe r ');
el.textContent = 'Leve 1 passed: ' + has Passed;
result:
level 1 passed : true
=======
text:
Headings :
<h1>This is a Main Heading</h1>
<h2>This is a Level 2 Heading</h2>
<h3>This is a Level 3 Heading</h3>
<h4>This is a Level 4 Heading</h4>
<h5>This is a Level 5 Heading</h5>
<h6>This is a Level 6 Heading</h6>
results is:
This is a Main Heading
This is a Level 2 Heading
This is a Level 3 Heading
This is a Level 4 Heading
This is a Level 5 Heading
This is a Level 6 Heading
Paragraphs :
<p>this is a paragraph</p>
result:
this is a paragraph
Bold & Italic:
<b> this is bold <b>
<i> this is italic <i>
result:
this is bold
this is italic
Superscript & Subscript :
<sub></sub>
<sup></sup>

When the browser comes across two or more spaces next to each
other, it only displays one space.
Similarly if it comes across a line
break, <br/> it treats that as a single space too. This is known as
white space collapsing.
Quotations:
<blockquote>p>Did you ever stop to think, and forget to start
again? </blockqoute>
result:
p>Did you ever stop to think, and forget to start again?
Changes to Content:
<ins> show content that has been inserted into a document
<del>show text that has been deleted from document.
<s> is no longer accurate or relevant (strike through)
introduction to css :
CSS treats each HTML element as if it appears inside its own box and uses rules to indicate how that element should look.
BLOCK & INLINE ELEMENTS :
Block level elements look like they start on a new line.
Examples include the <h1>
Inline elements flow within the text and do not start on a new
line. Examples include <b>
CSS works by associating rules with HTML elements , A CSS rule contains two parts: a selector and a declaration.

using css can be done by 3 ways :
1- Using External CSS <link>
2- Using Internal CSS <style>
3- inline css using style attribute
java script
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one. Each individual instruction or step is known as a statement .
Expressions evaluate into a single value.
JAVASCRIPT IS CASE SENSITIVE
1- COMMENTS:
explain what your code does. They help make your code easier to read and understand.
/* Th i s script displays a greeting to the user based upon the current time.
It is an example from JavaScript & jQuery book */
2- variables:
You can compare variables to short-term memory, because once you leave the page, the browser will forget any information it holds.
syntax

there is many types of varibles :

3- OPERATORS:
- ARITHMETIC OPERATORS :

- COMPARISON OPERATORS :

decision-making :
Decision Making statements are** if, else, elseif** and switch these statements are used in making decisions.
there are 2 components to a decision:
1- evaluate of a condition usually done by comparing 2 values using comparison operators.
2- conditional statment if the condtion is met then then the code excute
![decision] (https://i.pinimg.com/originals/d5/da/e2/d5dae2c20b84d9f5b19038de2d38796d.jpg)
var pass = 50; // Pass mark
var score = 90; // Score
// Check if t he user has passed
var hasPas sed = score >= pass ;
// Wr ite the message i nto the page
var el = document .getElementByld(' answe r ');
el.textContent = 'Leve 1 passed: ' + has Passed;
result:
level 1 passed : true
4afde8d50a1f09ecd2643f45cb50e8b6fd76b6ff