Reading-notes
java script :
A script is a series of instructions that the computer can follow in order to achieve a goal.
When you use JavaScript in the browser, there is a part of the browser that is called an interpreter (or scripting engine). The interpreter takes your instructions (in JavaScript) and translates them into instructions the browser can use to achieve the tasks you want it to perform, each line of code is translated one-by-one as the script is run.
## You can use JavaScript to select any element, attribute, or text from an HTML page, You can use JavaScript to add elements, attributes, and text to the page, or remove them.
# html : HTML Uses Elements to Describe the Structure of Pages , Each element has an opening tag and a closing tag. Tags act like containers. They tell you something about the information that lies between their opening and closing tags.
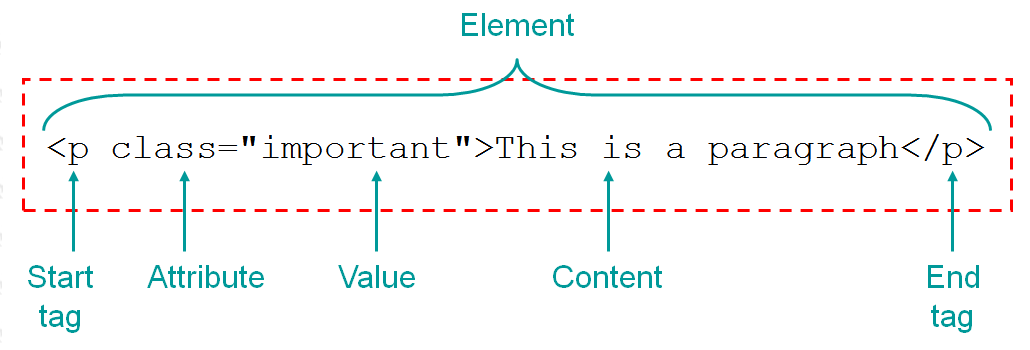
** Attributes ** provide additional information about the contents of an element. They appear on the opening tag of the element and are made up of two parts: a name and a value, separated by an equals sign.
## id attribute : giving an element a unique identity allows you to style it differently than any other instance of the same element on the page. The id attribute is known as a global attribute because it can be used on any element.
## class attribute : rather than uniquely identifying one element within a document, you will want a way to identify several elements as being different from the other elements on the page. ## block level elements: elemnts that appear to start on a new line in the browser window.
example: <h1>
## inline elements: elemnts that appear to continue on the same line as their neighbouring elements.
example : <img>
## grouping elemnts :
<div>
The<div>element allows you to group a set of elements together in one block-level box.<span>Contain a number of inline elements
## <iframe> :
content of the iframe can be any html page
example:
<iframe
width="450"
height="350"
src="http://maps.google.co.uk/maps?q=moma+new+york
&output=embed">
</iframe>
Information About Your Pages :
<meta>
The <meta> element lives inside the <head> element and contains information about that web page.
The <meta> element is an empty element so it does not have a
closing tag.
There are some characters that are used in and reserved by HTML code :
- © ——>
© - ® ——->
® - ™——>
™
The new HTML5 elements
indicate the purpose of different parts of a web page and help to describe its structure :
<header> <footer><nav>The <nav> element is used to contain the major navigational blocks on the site such as the primary site navigation.<article><aside><section><hgroup>group together a set of one or more <h1> through <h6> elements so that they are treated as one single heading.<figure> <figcaption>## Where there is no suitable element to group a set of elements, the<div>element will still be used.
## when building a webstie : 1- who your target audienceis.
2- why they would come to your site.
3- what information they want to find and when they are likely to return.
## site strucutre using :
- Site maps : allow you to plan the structure of a site.
- Wireframes : allow you to organize the information that will need to go on each page.