Reading-notes
random module in Python
provides access to functions that support many operations.
Random functions
1-Randint
(If we wanted a random integer)
accepts two parameters: a lowest and a highest number. Generate integers between them
import random
print random.randint(0, 5) // This will output either 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5
2-Random (to get larger numbers)
import random
random.random() * 100
3-Choice (Generate a random value from the sequence sequence.)
import random
myList = [2, 109, False, 10, "Lorem", 482, "Ipsum"]
random.choice(myList)
4-Shuffle ( shuffles the elements in list in place, so they are in a random order)
from random import shuffle
x = [[i] for i in range(10)]
shuffle(x)
Output:
# print x gives [[9], [2], [7], [0], [4], [5], [3], [1], [8], [6]]
5-Randrange (Generate a randomly selected element from range(start, stop, step))
random.randrange(start, stop[, step])
import random
for i in range(3):
print random.randrange(0, 101, 5)
# Risk Analysis
## Why use Risk Analysis?
1- highlights the potential problem areas.
2-helps the developers and managers to mitigate the risks.
unavoidable. risks
there are certain risks that are unavoidable.
ex : The time that you allocated for testing
you have to tackle the situation with care. steps: 1-Conduct Risk Assessment review meeting
2-Use maximum resources to work on high-risk areas
3- Create a Risk Assessment database for future use
4- Identify and notice the risk magnitude indicators: high, medium, low.
Risk Identification:
-
Business Risks: It is the risk that may come from your company or your customer, not from your project.
-
Testing Risks
-
Premature Release Risk: analyze the risk associated with releasing unsatisfactory or untested software is required
-
Software Risks: risks associated with the software development process.
Risk Assessment
( assessment has to be dealt programmatically)
-
Effect determine the impact of the action
-
Cause Initialize scanning the problem and reach to the point that could be the most probable reason behind that
-
Likelihood there is a probability that a requirement won’t be satisfied.
How to perform Risk Analysis?
1-Searching the risk
2- Analyzing the impact of each individual risk
3- Measures for the risk identified
TestCoverage
(also called code coverage)
Test coverage is a useful tool for finding untested parts of a codebase.
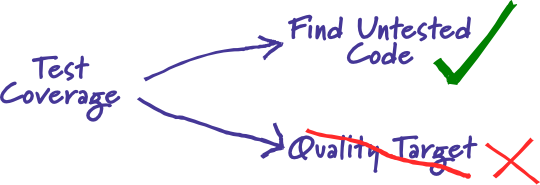
high coverage numbers are too easy to reach with low quality testing.
TDD is a very useful, but certainly not sufficient,
I would expect a coverage percentage in the upper 80s or 90s. I would be suspicious of anything like 100%
**The reason why people focus on coverage numbers is because they want to know if they are testing enough. **
low coverage numbers, say below half, are a sign of trouble. But high numbers don’t necessarily mean much, and lead to ignorance-promoting dashboards.
You are testing too much if you can remove tests while still having enough.
You can always move slow tests to a later stage in your deployment pipeline, or even pull them out of the pipeline and run them periodically.
### video ##
## how to calculate big O 1- different steps get add (ex: loops ) 2- drop constants( there is no 2n or 3n only powers of n) 3- different parts have different names 4- drop non domenant term