Reading-notes
Linear regression
(find a function that maps some features or variables to others sufficiently well.)
It contains function for regression, classification, clustering, model selection and dimensionality reduction.
in regression analysis, you usually consider some phenomenon of interest and have a number of observations. Each observation has two or more features. Following the assumption that (at least) one of the features depends on the others, you try to establish a relation among them.
sklearn.linear_model module which contains “methods intended for regression in which the target value is expected to be a linear combination of the input variables”.
The dependent features are called the dependent variables, outputs, or responses.
The independent features are called the independent variables, inputs, or predictors.
When Do You Need Regression?
1-answer whether and how some phenomenon influences the other or how several variables are related.
2- to forecast a response using a new set of predictors
Linear Regression
( One of its main advantages is the ease of interpreting results)
Regression Performance
Simple Linear Regression
Simple or single-variate linear regression is the simplest case of linear regression with a single independent variable, 𝐱 = 𝑥.

Multiple Linear Regression
Multiple or multivariate linear regression is a case of linear regression with two or more independent variables.
It represents a regression plane in a three-dimensional space. The goal of regression is to determine the values of the weights 𝑏₀, 𝑏₁, and 𝑏₂ such that this plane is as close as possible to the actual responses and yield the minimal SSR.
Polynomial Regression
the polynomial dependence between the output and inputs and, consequently, the polynomial estimated regression function.
the simplest example of polynomial regression has a single independent variable, and the estimated regression function is a polynomial of degree 2: 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑏₀ + 𝑏₁𝑥 + 𝑏₂𝑥².
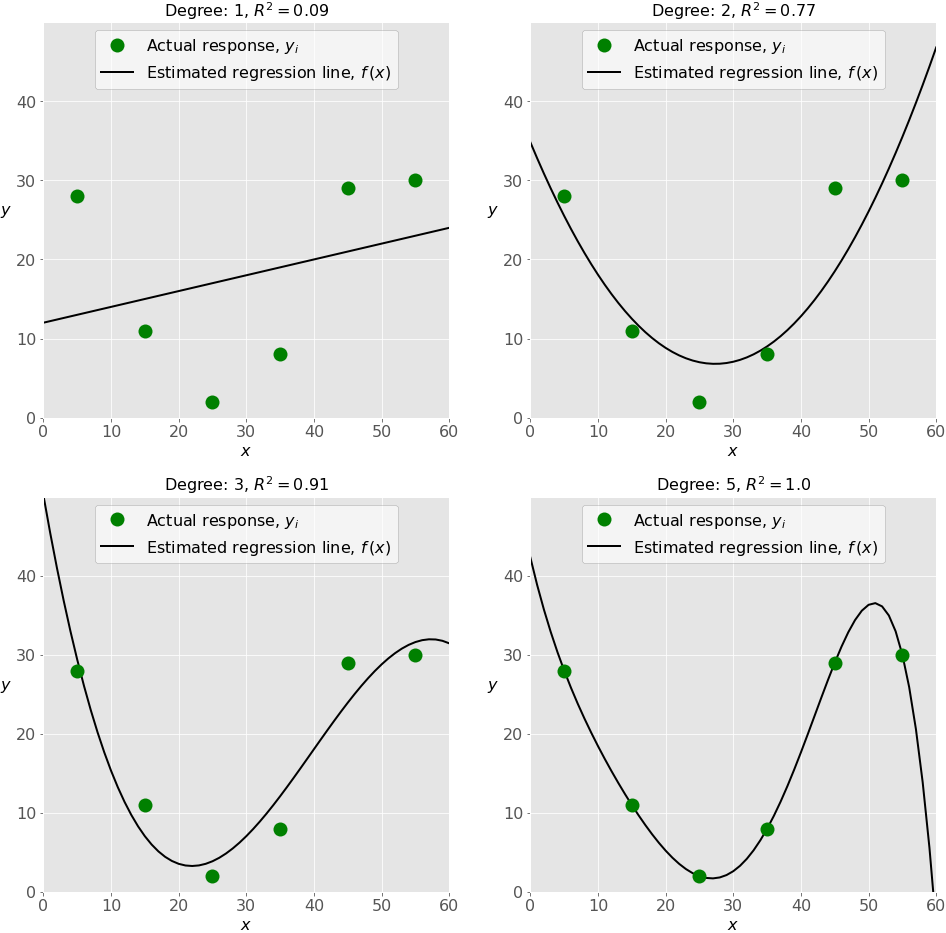
Underfitting and Overfitting
o the choice of the optimal degree of the polynomial regression function.
Underfitting occurs when a model can’t accurately capture the dependencies among data, usually as a consequence of its own simplicity. It often yields a low 𝑅² with known data and bad generalization capabilities when applied with new data.
Overfitting happens when a model learns both dependencies among data and random fluctuations. In other words, a model learns the existing data too well. Complex models, which have many features or terms, are often prone to overfitting. When applied to known data, such models usually yield high 𝑅². However, they often don’t generalize well and have significantly lower 𝑅² when used with new data.
Implementing Linear Regression in Python
The package NumPy is a fundamental Python scientific package that allows many high-performance operations on single- and multi-dimensional arrays.
There are five basic steps when you’re implementing linear regression:
Import the packages and classes you need.
Provide data to work with and eventually do appropriate transformations.
Create a regression model and fit it with existing data.
Check the results of model fitting to know whether the model is satisfactory.
Apply the model for predictions.
Beyond Linear Regression
Linear regression is sometimes not appropriate, especially for non-linear models of high complexity.
there are other regression techniques suitable for the cases where linear regression doesn’t work well. Some of them are support vector machines, decision trees, random forest, and neural networks.
The package scikit-learn provides the means for using other regression techniques in a very similar way to what you’ve seen. It contains the classes for support vector machines, decision trees, random forest, and more, with the methods .fit(), .predict(), .score() and so on.
Conclusion
Linear regression is implemented with the following:
- scikit-learn if you don’t need detailed results and want to use the approach consistent with other regression techniques
- statsmodels if you need the advanced statistical parameters of a model