Reading-notes
class 01
Component-Based Architecture:
component is a modular, portable, replaceable, and reusable set of well-defined functionality that encapsulates its implementation and exporting it as a higher-level interface.
Component-based architecture focuses on the decomposition of the design into individual functional or logical components that represent well-defined communication interfaces containing methods, events, and properties.
The primary objective of component-based architecture is to ensure component reusability
Component-oriented software design has many advantages such as :
-
Reduced time in market and the development cost by reusing existing components.
-
Increased reliability with the reuse of the existing components.
Views of a Component :
1-Object-oriented view : set of one or more cooperating classes
2- Conventional view : functional element or a module of a program that integrates the processing logic
3- Process-related view : he system is building from existing components maintained in a library.
examples:
- A user interface (UI) component includes grids, buttons
- components that are resource intensive
- invisible components
## Characteristics of Components:
1- Reusability : reused in different situations in different applications. However, some components may be designed for a specific task.
2- Replaceable − Components may be freely substituted with other similar components.
3- Not context specific − Components are designed to operate in different environments and contexts.
4- Extensible − A component can be extended from existing components to provide new behavior.
5- Encapsulated − A component depicts the interfaces, which allow the caller to use its functionality, and do not expose details of the internal processes or any internal variables or state.
6- Independent − Components are designed to have minimal dependencies on other components.
Principles of Component−Based Design :
1- The software system is decomposed into reusable, cohesive, and encapsulated component units.
2- Each component has its own interface that specifies required ports and provided ports; each component hides its detailed implementation.
3- A component should be extended without the need to make internal code or design modifications to the existing parts of the component.
4- Depend on abstractions component do not depend on other concrete components, which increase difficulty in expendability.
5- Connectors connected components, specifying and ruling the interaction among components. The interaction type is specified by the interfaces of the components.
6- Components interaction can take the form of method invocations, asynchronous invocations, broadcasting, message driven interactions, data stream communications, and other protocol specific interactions.
7- For a server class, specialized interfaces should be created to serve major categories of clients. Only those operations that are relevant to a particular category of clients should be specified in the interface.
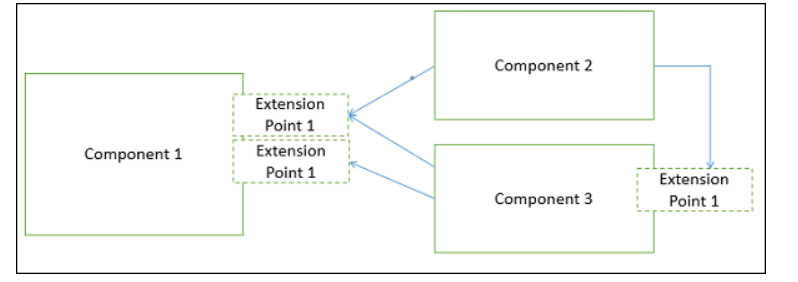
8- A component can extend to other components and still offer its own extension points. It is the concept of plug-in based architecture. This allows a plugin to offer another plugin API.
Component-Level Design Guidelines:
component names from the problem domain and ensures that they have meaning to all stakeholders who view the architectural model.
Extracts the business process entities that can exist independently without any associated dependency on other entities.
Recognizes and discover these independent entities as new components.
Uses infrastructure component names that reflect their implementation-specific meaning.
Models any dependencies from left to right and inheritance from top (base class) to bottom (derived classes).
Model any component dependencies as interfaces rather than representing them as a direct component-to-component dependency.
Conducting Component-Level Design:
1- Recognizes all design classes
2- Describes all design classes
3- Identifies appropriate interfaces for each component
4- Describes processing flow within each operation in detail by means of pseudo code or UML activity diagrams.
5- Describes persistent data sources (databases and files) and identifies the classes required to manage them.
6- Develop and elaborates behavioral representations for a class or component.
7- Elaborates deployment diagrams to provide additional implementation detail.
8- Demonstrates the location of key packages or classes of components in a system by using class instances and designating specific hardware and operating system environment.
9- The final decision can be made by using established design principles and guidelines.
Advantages of Components
1-Ease of deployment
2- Reduced cost
3- Ease of development
4- Reusable
5- Modification of technical complexity
6- Reliability
7-System maintenance and evolution
8- Independent
React’s Props
“Props” is a special keyword in React, which stands for properties and is being used for passing data from one component to another.
data with props are being passed in a uni-directional flow. (one way from parent to child) props data is read-only, which means that data coming from the parent should not be changed by child components.props data is read-only, which means that data coming from the parent should not be changed by child components.
## Using Props in React:
1- define an attribute and its value(data).
<ChildComponent text={“I’m the 1st child”} />
2- pass it to child component(s) by using Props.
const ChildComponent = (props) => {
return <p>I'm the 1st child!</p>;
};
3- render the Props Data.
const ChildComponent = (props) => {
return <p>{props.text}</p>;
};